Table of Contents
Short on time? Here’s what to expect from the article:
- Stock trading is the act of purchasing or selling equities of companies
- Bid and ask prices, spreads, and the role of market makers and market takers are crucial concepts for new investors
- Understand the key types of orders and how order duration affects trade execution for investors.
Achieving financial security and building long-term wealth is a priority for many. To this end, it is essential to consider investment avenues that provide inflation-beating returns. And equities, perhaps, are one of the most popular and effective means of achieving the same.
Equities being inherently volatile instruments, however, it is equally important to understand just how stock trading works. The following article helps you do just that.
Basics of stock trading
Stock trading involves the sale and purchase of shares of publicly listed companies through a regulated exchange. Investing in stocks, in essence, means you holding a portion of a given company. This ownership allows you to take part in the company’s growth story, and benefit from the profits it may potentially generate.
When a company performs well, there are two means of returns for investors: capital appreciation (via an increase in share prices), and dividend payments.
Before going ahead, however, one must note that stocks are also exposed to higher volatility levels, driven by external factors such as economic conditions, shifts in market sentiment, and internal company developments.
Understanding bid price and ask price
In stock trading, the terms “bid” and “ask” represent the immediate market value of a stock.
- Bid refers to the price at which investors can sell equities.
- Ask is the price at which investors can purchase equities.

What spreads in stock trading are, and why they matter
The difference between bid and ask prices is called the spread. A small spread generally means that the stock is liquid and actively traded. Conversely, a bigger spread signals low activity; this means fewer people are interested, making those shares hard and costly to move.
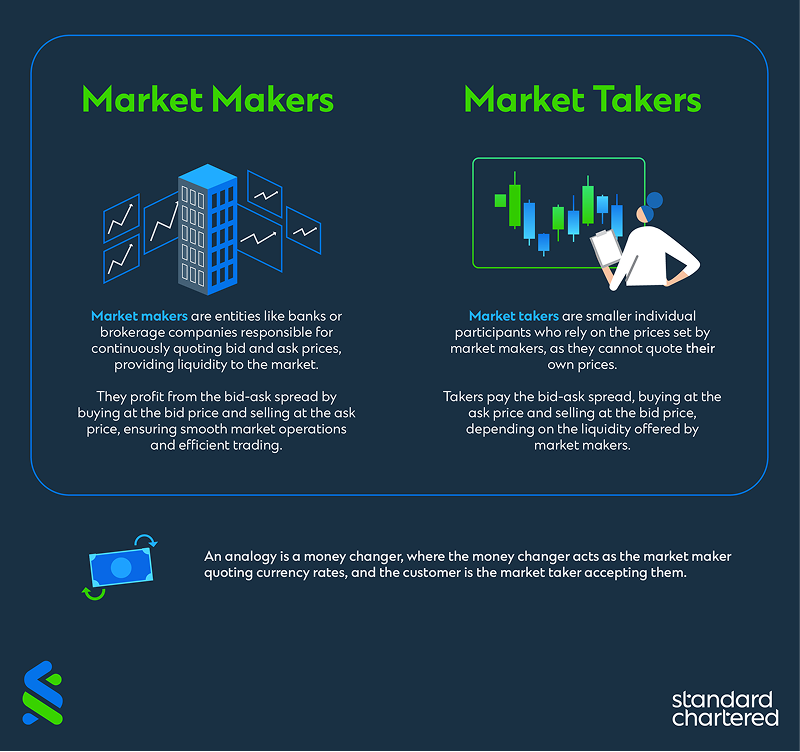
Stock trading roles: Market makers and traders explained
Entities like banks and brokerage companies that continuously quote buy and sell prices for stocks are called market makers. They create the market by facilitating liquidity and ensuring orderly trading. On the other hand, individual traders and small companies are known as market takers.
These act immediately by accepting the best available price. Think of them as a client who walks into a shop and buys at the listed price without negotiating.
Types of orders
An order is a set of instructions given by the investors to buy or sell a particular stock. Orders can be made to a broker, brokerage firm or through an online stock trading platform. The main types of orders are listed below.
- Market order: A market order refers to buying or selling stocks at the current market price, provided there is enough volume. It is fast, but you cannot control the exact price.
- Limit order: In a limit order, you buy or sell at a particular price or better. So, you set your own price and wait; the trade is executed only if the market reaches that price.
- Stop loss order: Stop loss orders are used to automatically sell or buy stocks when they hit a certain price. This set price is referred to as the trigger price. Once your stock reaches the trigger price, your order gets activated to stop further losses.
Order duration: When to hold and sell
When investing in a stock, you can choose how long the order should remain active. Orders can have different durations:
- Good till cancel (GTC): A GTC order is an order given to buy or sell stocks that stay active until it is either executed or manually cancelled by the investor or broker.
- Good till day (GTD): In this type of order, the investor can instruct the broker to keep the order valid for a particular trading day. If the order is not executed by market closing time, it gets automatically cancelled.
Navigating the stock market requires a sound knowledge of its fundamental concepts as well as awareness of the associated risks. This can help make your investment journey a less stressful one, and your portfolio more resilient to market fluctuations. It is also important to evaluate your financial situation, investment horizon, and risk tolerance before engaging in stock trading.
If you are ready to put these stock trading concepts into practice, explore our digital investing platform. With SmartStocks, you can invest in global stocks, place and track orders online, and have a seamless trading experience.



