

Table of Contents
- Rethinking fixed income: Sukuk as an ethical evolution in bond markets
- Beyond appearances: How sukuk fundamentally differs from conventional bonds
- Structuring sophistication: sukuk formats tailored for purpose
- Designing defensive income: Where sukuk sits in sophisticated portfolios
- Global traction: How institutional momentum is reshaping sukuk markets
- Confidence and security: Challenging misconceptions around sukuk safety
- Final thoughts: Aligning conviction with structure
Short on time? Here’s what to expect from the article:
Sukuk presents a Shariah-compliant alternative to traditional bonds, offering asset-backed returns rooted in real economic activity. This article explores key sukuk structures, their role in portfolio diversification, and rising global adoption—particularly among ESG-focused and high-net-worth investors. It highlights how sukuk blends ethical integrity with strategic income potential in today’s uncertain markets.
Rethinking fixed income: Sukuk as an ethical evolution in bond markets
Sukuk, also known as Islamic bonds, is Shariah-compliant, asset-backed instrument designed to generate returns through tangible economic activities such as leasing, trading, or partnerships. Unlike traditional fixed income options, sukuk is rooted in the principles of risk-sharing, transparency, and responsible investment.
For high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors alike, sukuk provides an elegant solution that blends capital preservation with values-based mandates. They appeal to those seeking stability without compromising ethical convictions, particularly in portfolios designed to weather long-term economic uncertainty.
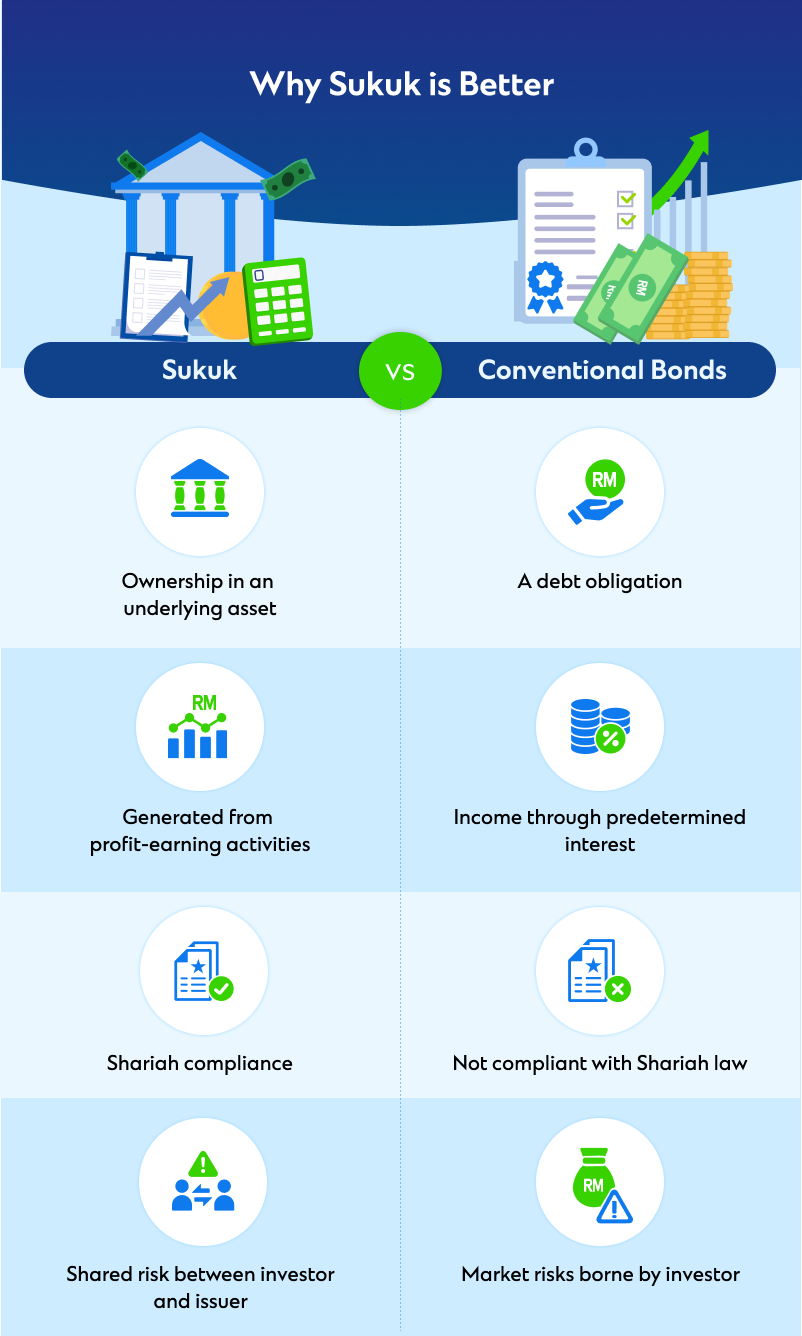
Beyond appearances: How sukuk fundamentally differs from conventional bonds
At a glance, sukuk and conventional bonds may seem similar—but their foundational structures diverge sharply. Sukuk represents ownership in real assets or business ventures, while conventional bonds are debt-based instruments that involve interest payments and lending arrangements.
Key distinctions include:
- Return generation: Sukuk yields returns through asset-linked profits such as rent or trade margins. Conventional bonds rely on fixed or floating interest payments.
- Risk distribution: Sukuk embeds shared risk between issuer and investor. Conventional bonds typically assign repayment obligations solely to the issuer.
- Ethical integrity: Sukuk excludes speculative activities and avoid industries or contracts considered non-compliant under Islamic principles.
These differences go beyond religious preference—they shape how sukuk behaves under market stress and influence how they are positioned in long-term portfolio strategies.
Structuring sophistication: sukuk formats tailored for purpose
The sukuk market offers a range of structures to suit varying investment goals and risk appetites:
- Sukuk al-Ijarah: Based on leased assets, generating predictable rental flows.
- Sukuk al-Murabahah: Trade-based instruments with pre-agreed profit margins.
- Sukuk al-Musyarakah: Joint venture models enabling profit and loss sharing.
- Sukuk al-Istisna: Structured around staged infrastructure or development projects.
These instruments are governed by established local and international standards. In Malaysia, sukuk structures are regulated by BNM and the Securities Commission Malaysia (SC), which set Shariah and capital market compliance frameworks.
On a broader scale global consistency is maintained through standards issues by the Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI) and the Islamic Financial Services Board (IFSB). Together, these frameworks enhance investor confidence and facilitate cross-border recognition.
Discover curated options via Standard Chartered’s fund library, including faith-based investment solutions.
Designing defensive income: Where sukuk sits in sophisticated portfolios
In today’s uncertain environment, sukuk is gaining traction as resilient components within diversified portfolios. Their structural design helps mitigate volatility, particularly when markets are exposed to rising interest rates or geopolitical disruption.
Benefits include:
- Low correlation with equities and conventional bonds, aiding diversification.
- Real-economy income derived from underlying assets—not speculation or leverage.
- Inflation-linked potential, particularly in lease-based sukuk structures.
Sukuk also aligns naturally with long-term mandates such as endowments, family offices, and ESG-conscious portfolios seeking stability without compromising on values.
Explore our suite of wealth-building tools under Wealth Solutions.
Global traction: How institutional momentum is reshaping sukuk markets
Once seen as a niche segment, sukuk is now part of the global investment dialogue. Growth has been driven by consistent issuance across key jurisdictions, including:
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC): Sovereigns and corporates are active issuers, supported by deep domestic markets and strong regulatory frameworks.
- Malaysia: A global hub for sukuk innovation and Shariah governance.
- Indonesia and supranational institutions: Bringing cross-regional diversity and scale.
Sukuk linked to sustainability themes such as ESG and green projects are increasingly sought after by sovereign wealth funds, development banks, and responsible investment platforms.
Confidence and security: Challenging misconceptions around sukuk safety
A common perception is that conventional bonds, especially those issued from developed markets like China, are inherently safer. However, sukuk is designed to offer a distinct form of protection based on real asset ownership, transparent governance, and disciplined issuance practices.
Considerations that support sukuk as a secure option:
- Sovereign and quasi-sovereign issuers in the Middle East often maintain high credit ratings and robust economic backing.
- Asset backing and risk-sharing mechanisms reduce the likelihood of default-related losses.
- Shariah oversight and surplus transparency create accountability frameworks not always present in conventional debt markets.
In fact, sukuk is frequently issued by governments and institutions with proven fiscal responsibility and a history of honouring Shariah-compliant standards.
Final thoughts: Aligning conviction with structure
Sukuk is no longer positioned merely as alternatives to conventional fixed income—they are increasingly becoming a preferred choice for investors who value integrity alongside performance.
For those seeking a portfolio anchored in ethical conviction, financial clarity, and global reach, sukuk offers a path forward that bridges legacy, purpose, and resilience. In a market where principles matter more than ever, sukuk stands out not just as compliant—but as compelling.



