Table of Contents
Short on time? Here’s what to expect from the article:
– The factsheet is your essential guide, clarifying the fund’s goals, methods, and risk profile to ensure the investment suits an investor’s financial needs.
– It lets investors assess the manager’s track record, fees, and performance against its benchmark, and helps them avoid making decisions based solely on market hearsay.
– The factsheet helps investors avoid emotional pitfalls, such as chasing high-flying assets or relying too much on temporary historical gains.
The unit trust fund fact sheet is a powerful tool for investors to assess the viability and suitability of an investment. Investors who want to start investing in a unit trust can check the fund fact sheet, a condensed document that outlines the key facts of a specific investment product. It provides a comprehensive overview of the fund’s historical performance and characteristics. Investors can develop a sound investment strategy based on the fund’s risk indicators and other key details.
What to consider in a fund fact sheet
Let’s break down the different components of a unit trust fund sheet and take a closer look at what you should be looking for.
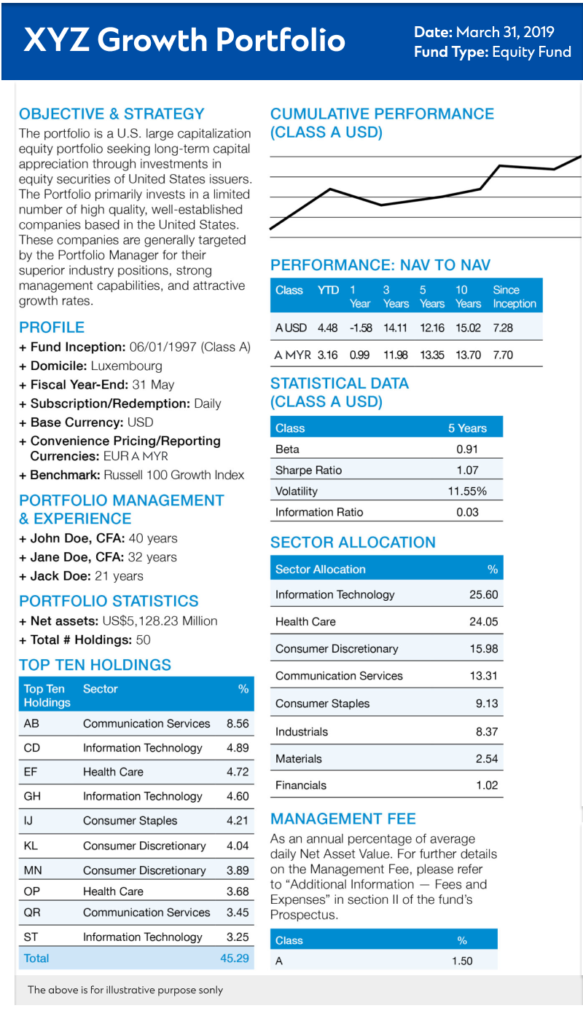
Investment objective and methodology
Fund Select follows a proprietary five-steps framework to assess, curate and continuously monitor market trends and the performance of each carefully selected fund. Aligned with Standard Chartered Advisory framework, it weaves in the concept of foundation and opportunistic investments to help investors put together a portfolio that can withstand different market conditions and drive long-term returns.
Fund manager details
Unit trusts are handled by experienced fund managers. To assess the credibility of a fund manager, investors can examine the performance of past investments managed by the fund manager.
Fund type
Malaysian unit trusts have various asset allocations, including debt or bonds, equity, money market funds, and Shariah funds, among others.
Asset allocation
Investors can understand how the fund allocates the resources among different asset classes, including bonds, equities, and other investment vehicles. Risk-averse investors usually prefer a bond fund. They can use the fund fact sheet to consider whether they prefer corporate bonds, which offer higher yields, or government bonds, known for their stability. Along with the fund performance chart, the fact sheet provides details on the industry breakdown and top holdings.
Geographic exposure
Evaluating a fund’s exposure to specific geographic regions and sectors is crucial for aligning the fund with global economic trends and the investor’s financial objectives.
Performance details
Although the past performance of a unit trust is no guarantee of its future performance, it is still helpful to compare a fund’s performance with that of other funds. Returns are typically shown over one-, three-, five-, and ten-year terms.
Risk tolerance
Investors can assess a fund’s risk profile and verify whether the required investment time horizon aligns with their personal needs. While long-term investors can endure greater volatility to receive potentially higher returns, short-term investors often prioritise stability. Therefore, before investing, it is essential to check how well the fund aligns with one’s risk tolerance.
Fund size
A large fund size (assets under management or AUM) often reflects investor confidence and a track record of success. In comparison, smaller funds can be more agile and may be better able to adapt to shifting market conditions. It is essential to recognise that various factors, including the size of the funds, can influence fund performance. However, before investing, investors can check the fund size and determine whether the total value of assets held within the fund aligns with their investment goals.
Fee details
Investments typically incur various fees. Investors can review the associated fees outlined in the factsheet, including the management fee (which covers personal fund management), the trustee fee (which covers the trustee’s role in safeguarding investor interests and ensuring compliance), and sales charges (which cover the service or commission provided by the fund managers).
Common mistakes one should avoid when investing
It is essential to avoid common pitfalls that hinder the decision-making process.
- Overemphasis on historical performance: Historical performance metrics are valuable, but relying solely on past performance to make an investment decision can be misleading, as market conditions change frequently.
- Predict the market movements: Market movements cannot be predicted correctly all the time. Hence, investors who try to time the market usually end up making emotion-driven decisions. In contrast, an investment should be made after a sound analysis.
- Overlook benchmark comparisons: Novice investors often fail to understand how a fund performs compared to its benchmark index. As a result, they usually miss the opportunity to optimise returns.



